How to authenticate and call the TeamCity API
April 2020
Overview
Below is two examples of authenticating to the TeamCity API with python. The two methods shown are token based authentication and username with password based authentication for a TeamCity server version before 2019.1.
This example uses the requests package which can be installed with the pip package manager. The untangle package has proven extremely helpful for working with the API as the response is returned in XML format.
Token based
This is the preferred way to authenticate with the API. A token can be created by clicking on the user name and selecting ‘Access Tokens’ then ‘Create Token’. Token based authentication was introduced in version 2019.1 so if you are using an older version of the server, the 2nd method below is required.
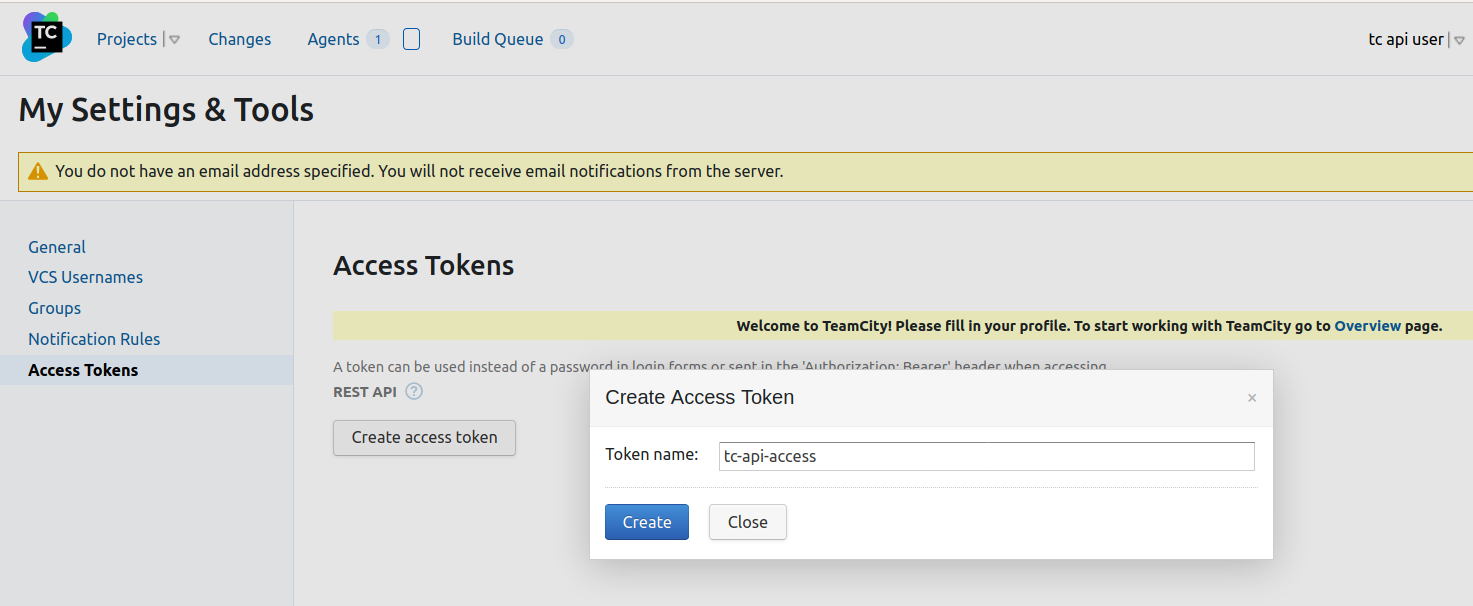
Now the token is created, it can be used to authenticate with the API by sending it in the headers.
The python code below (python3.6 and above to use the f string notation), shows how to create the header with a token that has been exported to the environment (export TOKEN=token_string).
import os
import requests
URL = 'https://teamcity.example.com'
TOKEN = os.getenv('TOKEN')
HEADERS = {
'Authorization': f'Bearer {TOKEN}',
'Content-Type': 'application/xml',
}
response = requests.get(url=URL,headers=HEADERS)
Username with Password
This method is reportedly slower than the token based approach above but is the only option on servers older than 2019.1.
It uses basic authentication of a username and password to authenticate and can be simply done with the following python code.
The url is slightly different from the token based url with ‘httpAuth’ being added.
import os
import requests
BASIC_URL = 'https://teamcity.example.com/httpAuth/app/rest/server'
HEADERS = {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
}
username = 'tc-api-user'
password = os.getenv('PASSWORD')
response = requests.get(url=BASIC_URL, auth=(username, password))
Basic queries
Now the user has been authenticated, we can get some basic information back. The examples below use the token based method, adjust the base url and get method to use the username and password authentication.
import os
import requests
BASE_URL = 'https://teamcity.example.com/app/rest/'
SERVER = f'{BASE_URL}server'
BUILD_QUEUE = f'{BASE_URL}buildQueue'
ROOTS = f'{BASE_URL}vcs-roots'
BUILDS = f'{BASE_URL}builds'
AGENTS = f'{BASE_URL}agents'
TOKEN = os.getenv('TOKEN')
HEADERS = {
'Authorization': f'Bearer {TOKEN}',
'Content-Type': 'application/xml',
}
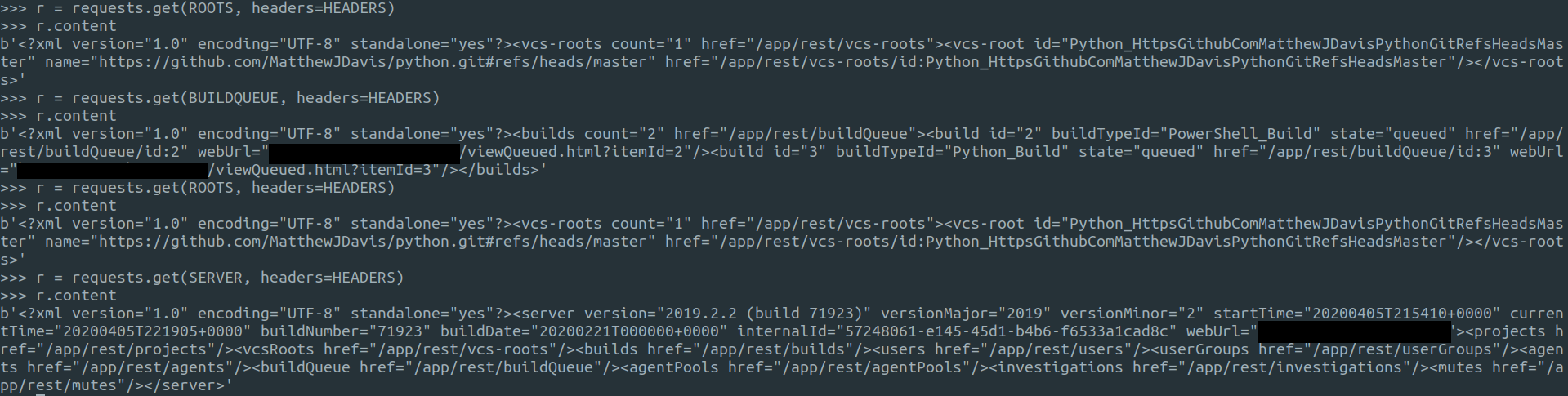
# Get agent details
r = requests.get(AGENTS, headers=HEADERS)
r.content
# Get build queue details
r = requests.get(BUILD_QUEUE, headers=HEADERS)
r.content
# Get server details (shows available endpoint)
r = requests.get(SERVER, headers=HEADERS)
r.content
Summary
Authenticating to the TeamCity API with Python is relatively straight forward once you figure out how to do it. From testing, I definitely recommend the token method, as the docs say, it does seem to have better performance when querying and then posting back.